Ngorongoro Crater National Park
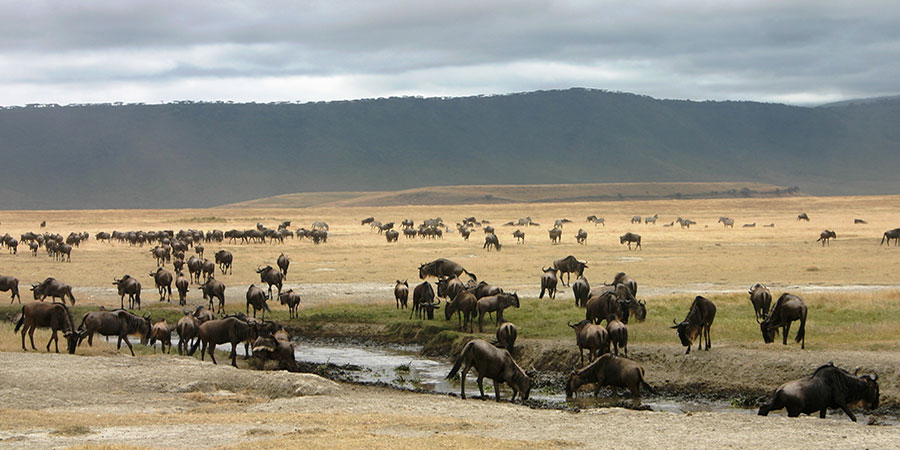
The Ngorongoro Crater is a world heritage site, the world’s largest intact volcanic caldera and is commonly referred to as the 8th wonder of the world.
The 2,000 feet high walls of the approximately 10 mile wide crater create a natural amphitheatre for the densest populations of large animals anywhere.
It is a microcosm of the vast Serengeti National Park and in one day it is possible to see a staggering array of East African wildlife including all the big carnivores.
The crater lives up to its infamous reputation with abundant and easily accessible wildlife and offers a reasonable chance to see lion, hyena or cheetah in action.
The Crater is truly awe-inspiring and will surely be one of the highlights of your safari.
The rim of the Ngorongoro Crater ranges in altitude from about 7,000 feet to 8,000 feet.
Down below, the relatively flat floor of the Crater rests at an elevation of about 5,500 feet
Ngorongoro Crater Wildlife Summary:-
The Ngorongoro Crater's rich soils and abundant, year-round water provide an ideal habitat for a variety of animals.
The Crater is not a self-contained ecosystem and some animals do migrate in and out but only in small numbers.
Most of the animals in the Crater are resident and remain year-round. There are approximately 20,000 large mammals at any given time within the Crater walls.
Herbivores that you will likely encounter include elephant, black rhino, hippo, buffalo, eland, zebra, wildebeest, hartebeest, waterbuck, warthog, Grant’s gazelle and Thomson’s gazelle.
Giraffe, impala and topi are strangely absent from the Crater floor, though they are common in the nearby Serengeti.
Although giraffes may find the descent into the Crater difficult, it is more likely that they are absent because there is not enough Jarma to browse.
It is not clear why topi or impala are missing.
Primates include baboons and vervet monkeys.
Carnivores that you will likely encounter include lion, cheetah, hyena and jackal. Leopards, servals, bat eared foxes and ratels are also resident within the Crater but are much more elusive.
Ngorongoro Crater Wildlife Fluctuations:-
Over the past 40 years since the early 1960s when long term studies began, the Crater has undergone drastic changes.
Wildebeest have historically made up at least half of the large animal population.
However, their numbers have been declining since the 1970s. Alternatively, buffalo have been on the rise as wildebeest numbers have decreased.
It is thought the departure of the Maasai and their livestock in the mid 1970s triggered this shift in wildebeest and buffalo populations.
Maasai regularly burned the grass in the Crater creating fresh green grass for their cattle, which may have benefited the wildebeest.
Now that the Maasai have departed, the grass is longer and coarser favoring the buffalos.
This fluctuation in large herbivores may have lead to a decrease in lion and hyena numbers which in turn allowed cheetahs to thrive.
The one thing that is for certain is that the Crater is truly a dynamic and ever changing ecosystem.
The Ngorongoro Crater Floor:-
The Ngorongoro Crater is sometimes called a microcosm of the Serengeti because there are five distinct habitats located in the relatively small area of the crater floor (100 square miles) that mirror the major habitats of its enormous neighbor, the Serengeti ecosystem (15,000 square miles). These habitats are as follows:
Lerai Forest is located in the southwestern section of the crater. Lerai is a Maasai word referring to the tall yellow barked acacias that dominate the forest. The forest is beautiful and is home to an array of animals including baboons, vervet monkeys, waterbucks and bushbucks. The forest is especially well known for its small population of giant tusker bull elephants. Lerai Forest is also home to the only leopards in the Crater. The leopards here are spotted on occasion but remain very much elusive. The best time to visit Lerai Forest is in the early morning.
In the central-western area is Lake Magadi (also known as Lake Makat), which plays host to thousands of migratory flamingos. The lake can be full of water or a dry expanse of white soda depending on the season.
The southeastern and northwestern sections of the crater are home to two large seasonal swamps. These areas are excellent for hippo and many species of water birds.
Spread throughout the central area of the crater is the short grass plains. These plains are home to thousands of wildebeest, zebra and Thomson’s gazelle. In the eastern section of the Crater are the longer grasslands where thousands of buffalo roam. One of smallest carnivores, the serval cat, is commonly found here in the tall grass.
The Ngorongoro Crater is the second best place in Tanzania (perhaps all of Africa) to view the large carnivores. The Serengeti is significantly better for large carnivores but nothing can simply compete with the Serengeti. Lion, cheetah, leopard, hyena, serval, ratel, jackal and bat eared fox all inhabit the Ngorongoro Crater. Lions, cheetahs, hyenas and jackals can usually be spotted but the other predators are much more elusive. As of 2004, it was estimated that there are 25-30 lions, 10-12 cheetahs and 50-60 hyenas inhabiting the Ngorongoro Crater. Note that these numbers do not include any cubs but refer strictly to adults, which are much easier to estimate. There are four prides of lions and six clans of hyenas on the Crater floor. It is interesting to note that all of today's crater lions are descended from only 15 lions that either survived or invaded the crater after a plague of biting flies in 1961.
As discussed in the ‘Wildlife Fluctuations’ section above, the Crater is a dynamic place and populations of certain species fluctuate widely over time. The increase of buffalos and decrease in wildebeest may have had a detrimental impact on both lions and hyenas as buffalo have been known to trample the young of both species. This has in turn allowed cheetahs to thrive in the Crater as lions are the number one cause of cheetah cub mortality. Typically in the past, cheetahs have not regularly settled in the Crater and lion and hyena numbers have been historically higher.